MIL-STD-1399-3OO8
§ ·
Line-to-line voltage tolerance (percent) = 1 Line - to - line voltage - Nominal user voltage 1x1OO
Where:
⎝ Nominaluser voltage ⎠
The line-to-line voltage is each line-to-line voltage and the nominal user voltage is provided in
Table I, item 7.
EQUATION 3
3.4.3 Voltage unbalance (line-to-line). The line-to-line voltage unbalance is the maximum deviation of any of the three line-to-line voltages from the average voltage divided by the average voltage. Voltages are either all rms or all peak (sinusoidal crest) values as shown in Equation 4.
§ ·
Line-to-line voltage unbalance (percent) = 1 Maximum deviation from the average voltage1x1OO
Where:
⎝ Averagevoltage ⎠
The average voltage is the sum of the line-to-line voltages divided by the number of line-to-line voltages.
EQUATION 4
3.4.4 Voltage modulation (amplitude). Voltage modulation is the periodic voltage variation (peak-to-valley) of a single line-to-line user voltage, calculated by Equation 5 and shown in Figure 3. The periodicity of voltage modulation should be considered to be longer than 1 cycle time at nominal frequency and less than 1O seconds. Voltages used in the following equation are either all rms or all peak (sinusoidal crest) values. Vnominal is provided in Table I, item 7.
V maximum - V minimum
Voltage modulation (percent) = 1 1 x1OO
§ ·
⎝ 2 x Vnominal ⎠
EQUATION 5
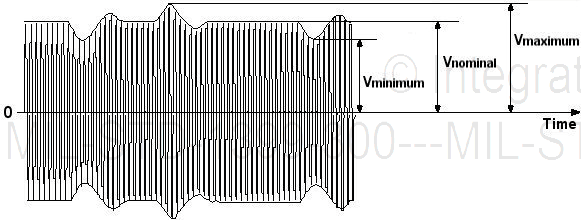
FIGURE 3. Voltage amplitude modulation.
6
For Parts Inquires call Parts Hangar, Inc (727) 493-0744
© Copyright 2015 Integrated Publishing, Inc.
A Service Disabled Veteran Owned Small Business